People with myasthenia gravis (MG) have weak muscles that get weaker as the day goes on. The neuromuscular system is affected by this autoimmune disease. Eyelids that hang down are often the first sign. In time, you may not be able to control your neck and limbs as well. The symptoms of this lifelong illness can be helped by medicines and surgery.
What is Severe Myasthenia?
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disease, which means that the body’s immune system attacks its own tissues by mistake. MG affects the way nerves and muscles talk to each other (the neuromuscular junction).
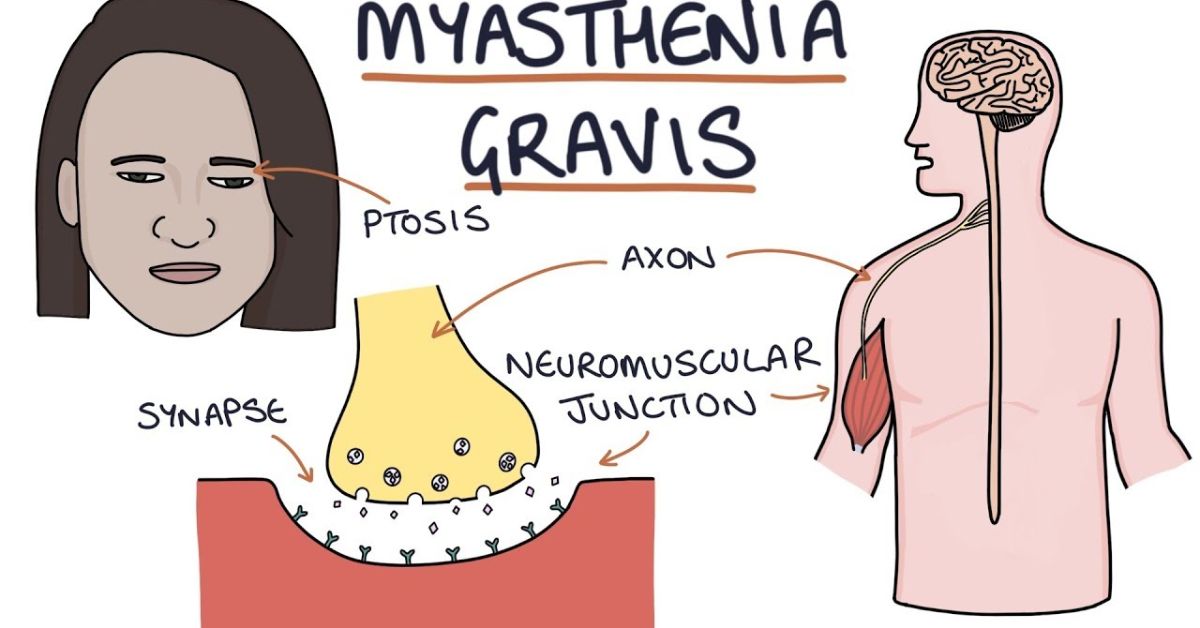
When someone has MG, they lose the ability to control their muscles on their own. They have different levels of muscle weakness and fatigue. They might not be able to move their eyes, faces, necks, or limbs. MG is a lifelong neuromuscular illness. There is no cure, but treatments can help, and some people may be able to get rid of the disease.
What Causes Myasthenia Gravis?
Your immune system hurts the receptors in your muscles, which is what causes myasthenia gravis. When you have myasthenia gravis, your immune system makes antibodies that stop the receptors from doing their job. This makes it harder for the chemical that travels from the nerve endings to reach the receptors. For your muscles to work right, they need this connection. Muscles get weak without it.
Click for more related updates
What Are The Symptoms of Myasthenia Gravis?
The eyes are often the first place to show signs of myasthenia gravis. Ptosis, or droopy eyelids, is the most common sign. This could hurt one eye or both. You may also feel more tired as the day goes on if you have myasthenia gravis.
Other signs of myasthenia gravis are:
- a weak feeling in the arms or legs
- trouble breathing, talking, chewing, or swallowing
Who Gets Myasthenia Gravis?
Myasthenia gravis is not caused by anything that we know of. People who have a history of myasthenia gravis in their family may be more likely to get it themselves. Women between the ages of 20 and 40 are more likely to get myasthenia gravis than men. After age 60, men are more likely to get the disease than women. But anyone of any age can get myasthenia gravis.
Myasthenia gravis can get worse when you are tired, sick, or stressed out. If you have myasthenia, talk to your doctor before taking any new medicine, whether it’s a prescription or something you buy at the store. Some medicines can make the symptoms of myasthenia gravis worse.
What Are The Symptoms Of Myasthenia Gravis?
To figure out if you have myasthenia gravis, your ophthalmologist can do tests like:
- a blood test to look for antibodies that shouldn’t be there
- Your brain and body will be checked for neurological problems.
- A nerve stimulation test looks at how your muscles’ electricity works.
- a test with edrophonium chloride, a drug that speeds up nerve activity. Your doctor will give it to you to see if your muscles get stronger for a short time.
How Is Myasthenia Gravis Treated?
Your eye doctor will work with a neurologist to figure out the best way to treat you. The treatment will depend on a number of things, such as the muscles that are hurt and how weak they are.
One or more of the following may be part of the treatment:
- Medicines that help nerves and muscles talk to each other better and make muscles stronger
- Medicines that make muscles stronger by stopping abnormal antibodies from being made
- a surgery to remove the thymus gland if your doctors think it might be causing the problem.
- plasmapheresis. This takes out the abnormal antibodies from the blood and puts normal cells in their place.
- intravenous immune globulin. This is a drug that can be made better by adding antibodies from donated blood.
Physical therapy and learning new ways to deal with problems may help make everyday life better.
Drop your emails in our comment section for the latest Updates.